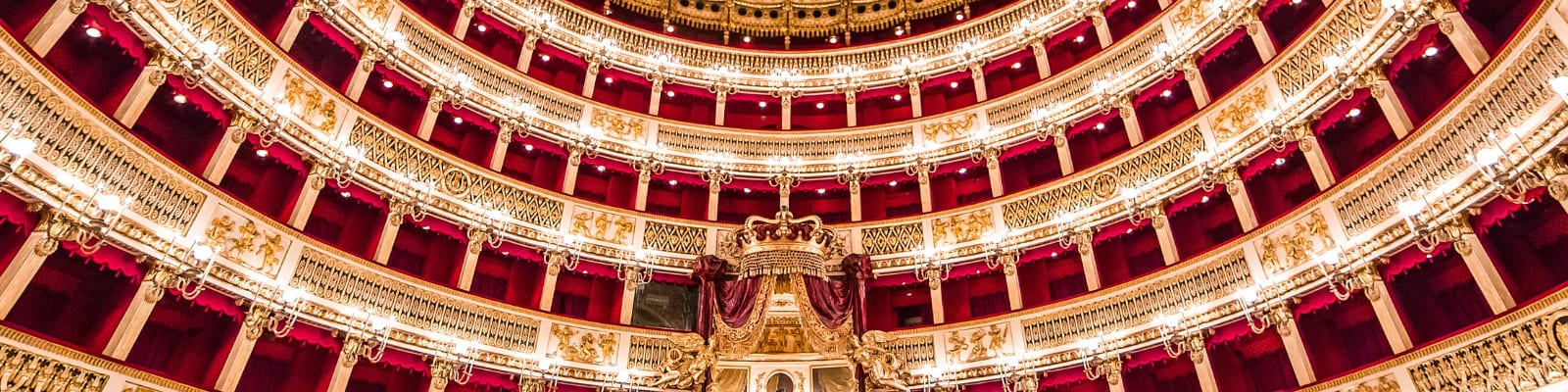


Opera, a dramatic art form that seamlessly combines music, singing, acting, and often dance, has captivated audiences for over four centuries. This grand spectacle has evolved alongside changes in musical styles, cultural tastes, and artistic innovations. For those new to opera, it is not just a performance but an immersive experience that offers a profound emotional journey. The powerful music, compelling stories, and striking visuals will sweep you away, connecting you to the characters' emotions and the drama of the story in a way that few other art forms can.
Meanwhile, seasoned opera buffs savor the intricate layers of musical composition, the historical context that shapes each piece, and the nuanced performances of skilled vocalists. They appreciate the detailed orchestration, thematic depth, and the evolution of styles that make each opera a unique masterpiece.
Whether you're just embarking on your opera journey or deepening your appreciation, the timeless allure of this art form always promises new and intriguing discoveries. As an audience member, you play an integral role in the opera experience. Your reactions and emotions are not just part of the immersive nature of the performance, they are a vital component that adds depth and richness to the entire experience.
Opera began in Italy at the end of the 16th century, with early works aiming to revive classical Greek dramas. These early operas, such as Jacopo Peri's "Dafne," were relatively simple compared to later standards, but they set the foundation for what was to come. Claudio Monteverdi, often considered the father of opera, brought greater musical complexity and emotional depth with works like "L'Orfeo," which remains a staple in the opera repertoire.
The Baroque period saw opera flourish, with composers experimenting with elaborate musical and theatrical techniques.Â
The Classical period brought clarity and emotional resonance to opera.
Romantic opera emphasized emotion, heroism, and dramatic storytelling.
The 20th and 21st centuries saw opera embrace new musical languages and multimedia elements.
By exploring these key elements and historical milestones, new audiences can appreciate opera's rich, multifaceted experience, engaging both the senses.
Music: The backbone of any opera, combining orchestral and vocal music.
Libretto: The text or script of the opera, often based on a play, book, or historical event.
Staging: The visual aspects, including sets, costumes, and lighting.
Operas are divided into acts, which are further divided into scenes. This structure helps to break down the narrative and provide pacing.
Opera is one of the most captivating and multifaceted art forms, combining various artistic elements into a singular, unforgettable experience. If you are new to opera, here is why it holds such a unique place in the world of performing arts. Its unique appeal lies in its ability to offer an immersive musical experience through its complex compositions and vocal brilliance, leaving you intrigued and eager to explore more.
Opera offers an immersive musical experience through its complex compositions and vocal brilliance. The music, composed by some of the greatest musical minds, such as Mozart, Verdi, and Wagner, tells a story with the orchestra setting the mood and enhancing the drama on stage. Opera singers, trained to project their voices over a full orchestra without microphones, use potent techniques that fill the entire theater and convey deep emotional depth. For example, Mozart's "The Magic Flute" features the famous "Queen of the Night" aria, showcasing incredible vocal agility and emotional intensity.
Attending an opera is a unique experience. Opera houses are often historic and grand, providing an immersive environment. The audience ranges from seasoned enthusiasts to curious newcomers, and while dress codes can vary, attending an opera is often seen as a special occasion. Operas can be longer than other performances, often including intermissions, allowing the audience to absorb and reflect on each act.
Opera continues to captivate audiences with its powerful combination of emotional depth, rich storytelling, and musical mastery. The intricate compositions and vocal prowess of performers stir profound feelings, while the elaborate sets and costumes provide a visual spectacle. This fusion of music, drama, and visual art, rooted in cultural heritage, ensures opera's enduring appeal and relevance.
Opera is a unique and enriching experience combining music, drama, and visual artistry. Understanding these elements can enhance your appreciation and enjoyment of this magnificent art form.

For many first-time listeners, the name Richard Wagner may initially evoke awe, curiosity, and perhaps a hint of hesitation. His operas are famously long, his stories mythic and layered, and his reputation as a revolutionary artist larger than life. The i
September 22, 2025

Richard Wagner was more than a composer - he was a force of nature who reshaped the very idea of what opera could be. Born in Leipzig in 1813, Wagner defied convention at every turn, fusing myth, music, poetry, and staging into something unprecedented.
September 19, 2025
A Cultural Journey Through Time Opera has been esteemed as a significant art form in Scandinavia for many years. It is characterized by the intricate integration of classical traditions with innovative contemporary performances.
December 27, 2024

The Renaissance was a period of profound transformation that ushered in a new era of creativity and expression. Among its many artistic innovations, opera stands out as a unique fusion of music, drama, and visual spectacle.
September 05, 2024

Opera, a dramatic art form combining music, singing, acting, and often dance, has captivated audiences for centuries. This guide aims to simplify opera's essential terms and concepts, making it accessible and engaging for beginners.
August 12, 2024